This package provides the following services:
atom-xterm
Atom plugin for providing terminals inside your Atom workspace.

Built in Terminal for Atom Feature Request
If you're reading this and you would rather see Atom have a built-in terminal by default, please go over to the built-in terminal feature request here, give it a thumbs up, and give an explanation as to why you need a built-in terminal in Atom by default.
Installation
To install, simply search for the atom-xterm package via Atom's package manager. It can also be installed via command-line with the apm command.
apm install atom-xterm
One time prerequisites
The atom-xterm package requires node-pty. That package currently requires building some native bindings on the local system using node-gyp. Providing prebuilt binaries is still work in progress so for now, you'll need to install certain packages on your system before installing atom-xterm. Below are what you'll need to install only once before installing atom-xterm.
Windows
Download and install Node.js. It's recommended to install the LTS version of Node.js.
Then, install the windows-build-tools package via npm.
npm install --global --production windows-build-tools
Linux
Debian/Ubuntu based Linux distributions
Follow the instructions here to install Node.js. It's recommended to install the LTS version of Node.js.
Then install the build-essential and python2.7 .deb packages.
sudo apt-get install build-essential python2.7
macOS
Install Node.js using the instructions provided here. Then, install the programs listed here
Usage
Opening Terminals
To open terminals, just open them through the menu.
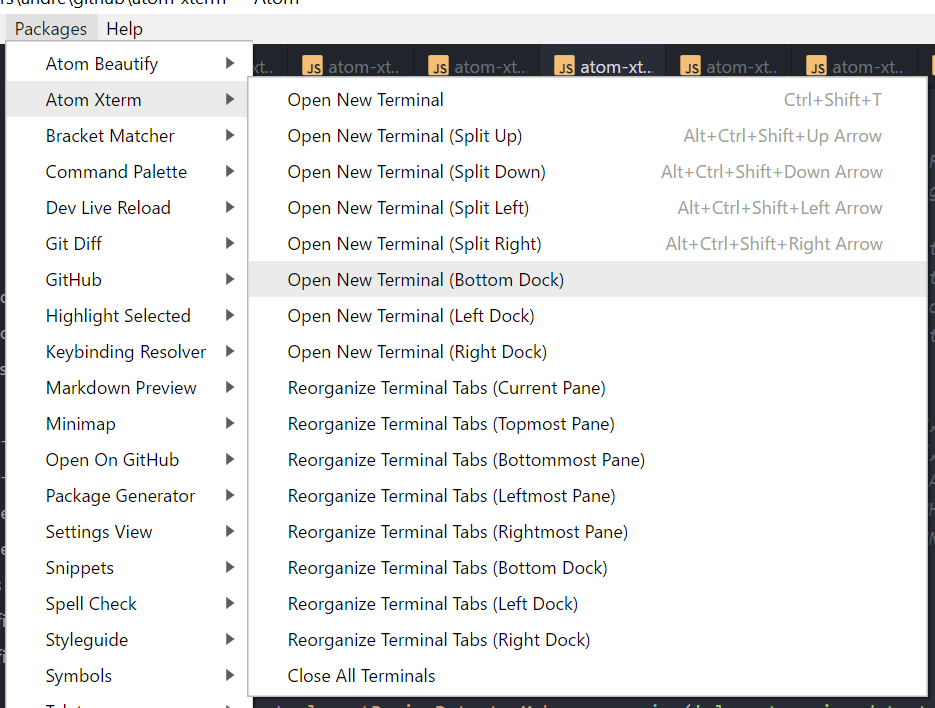
There's also various key bindings you can use to open terminals. See the available key bindings for the atom-xterm package.
There's also menu items available for opening terminals via right clicking on a text editor or on a terminal.
Finally, terminal tabs are automatically reopened at the spot you placed them when you last exited Atom.
Organizing Terminals
To quickly organize your terminal tabs, simply use the main menu. You can also find menu items by right-clicking on a terminal to organize your terminals.
And of course, there's the old fashion way of just moving the tabs where you want them. Feel free to place your terminal tabs anywhere in your workspace to include any of the docks.

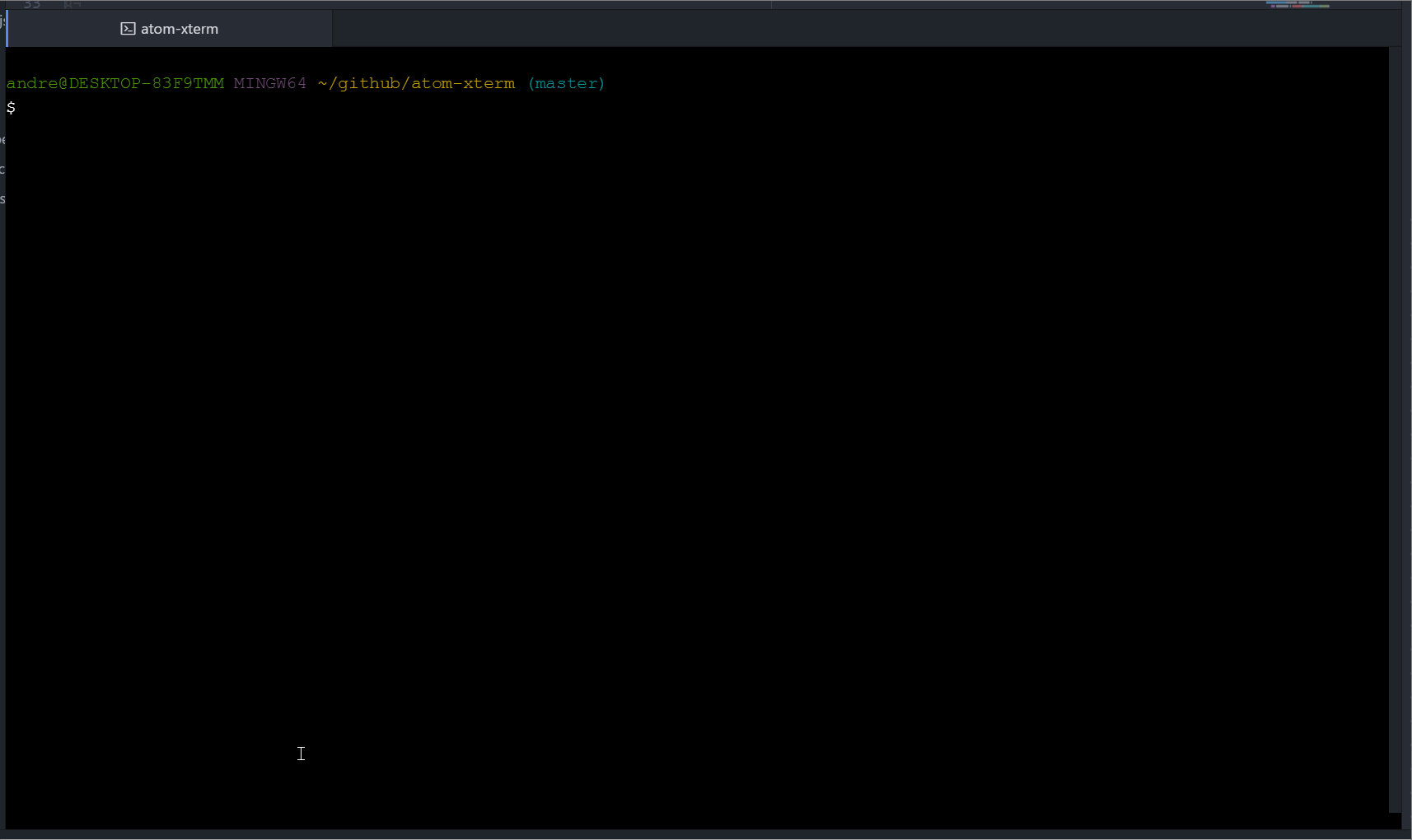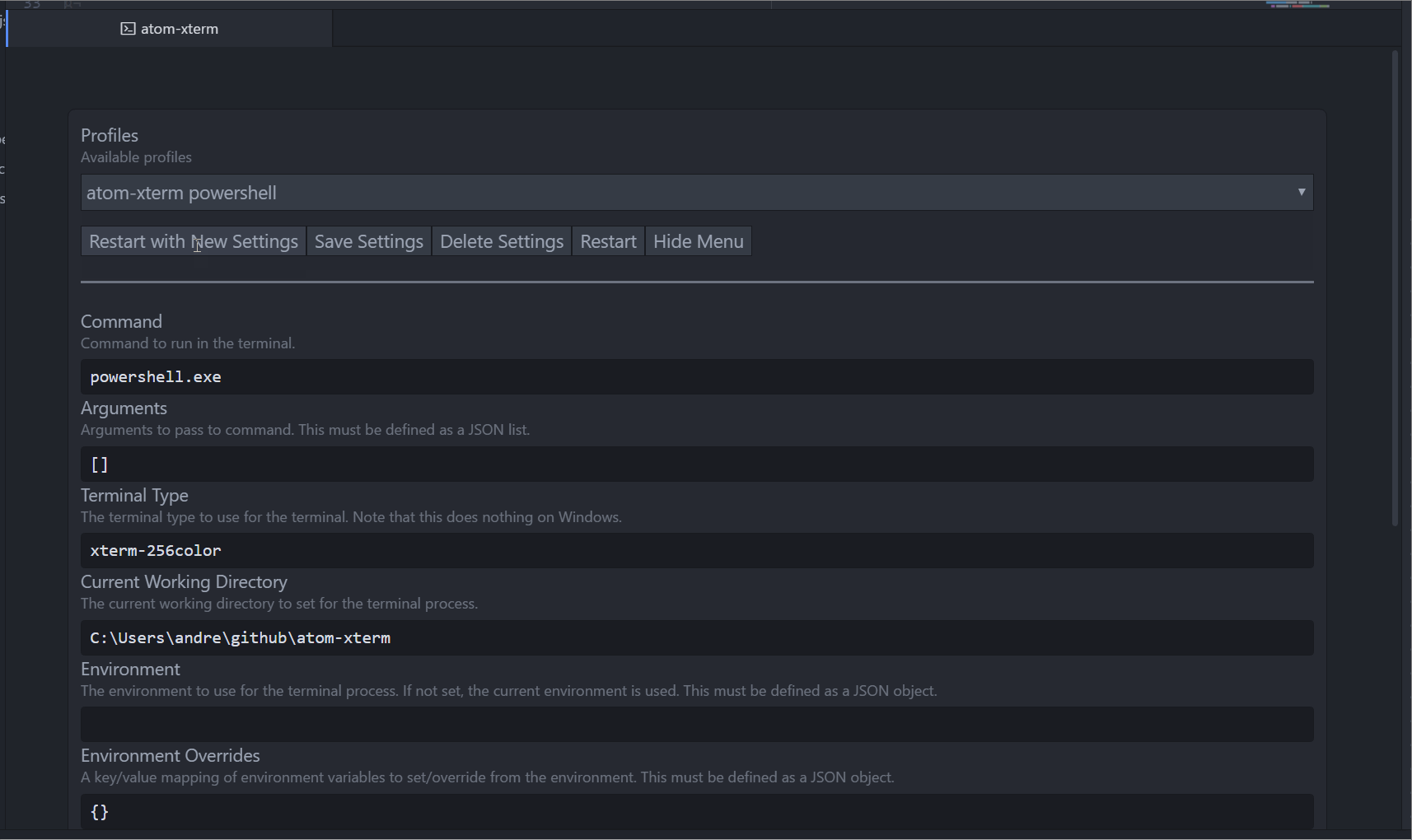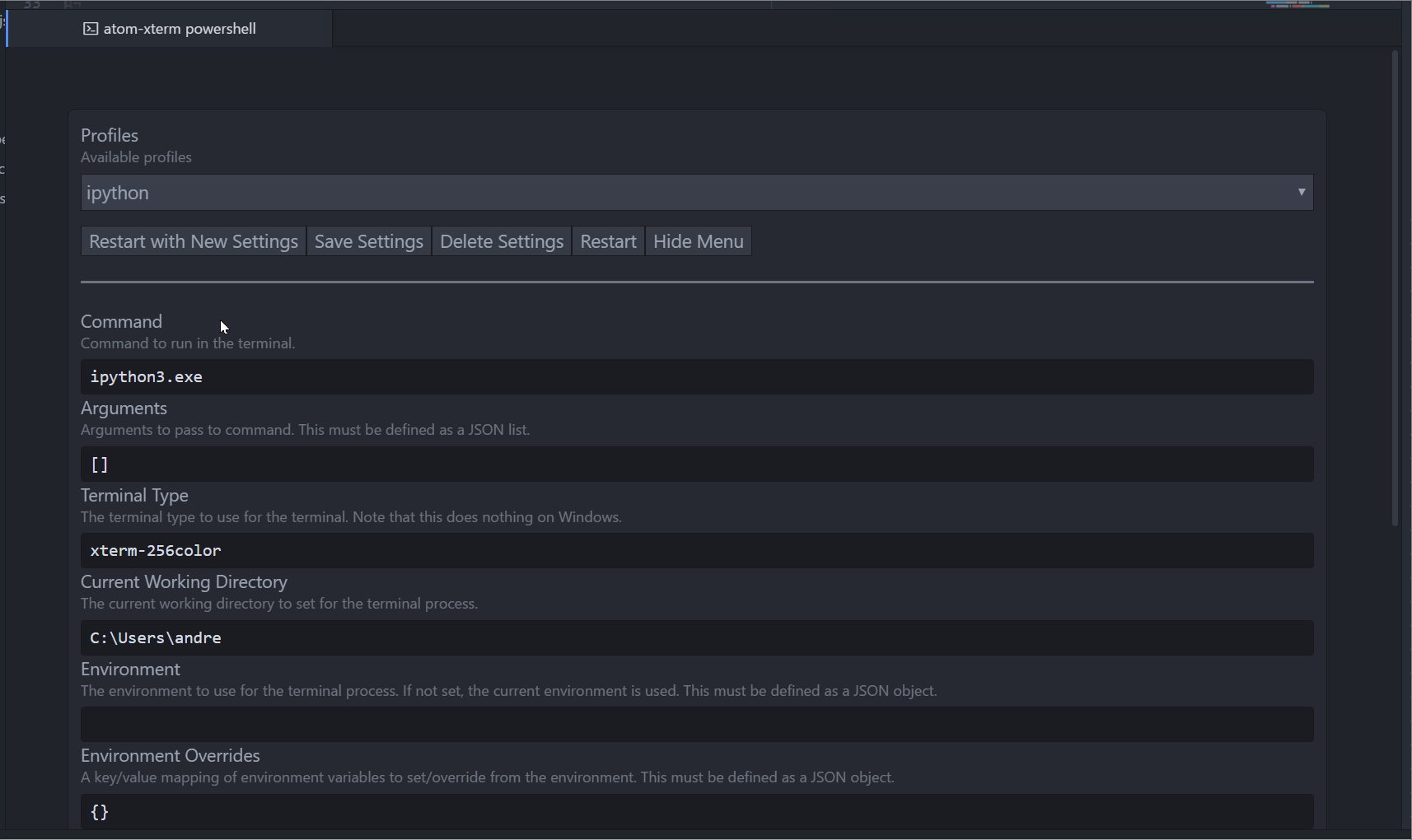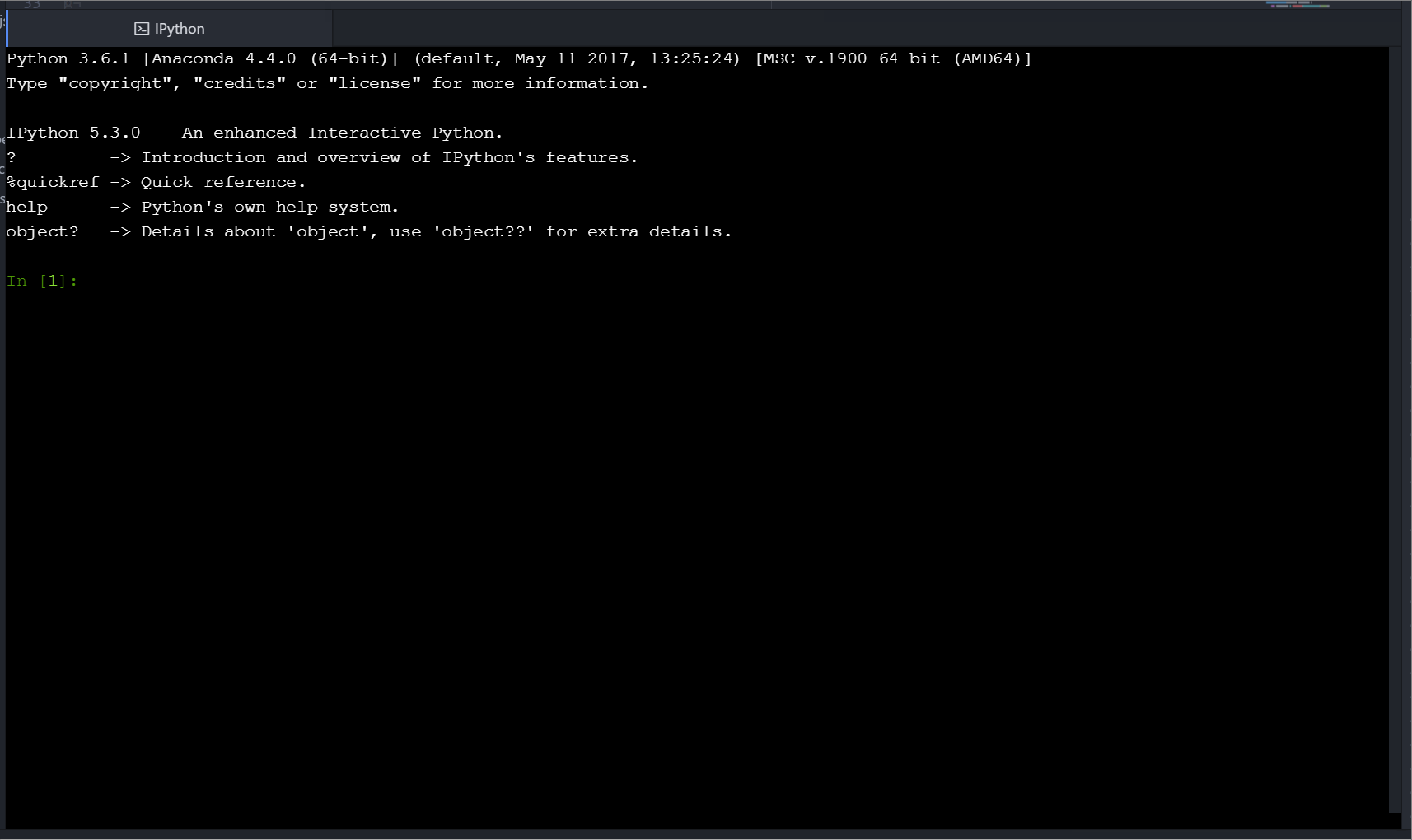
Profiles
The atom-xterm package supports saving and loading profiles. What this allows you to do is save commonly used commands and settings for later use.
Notifications
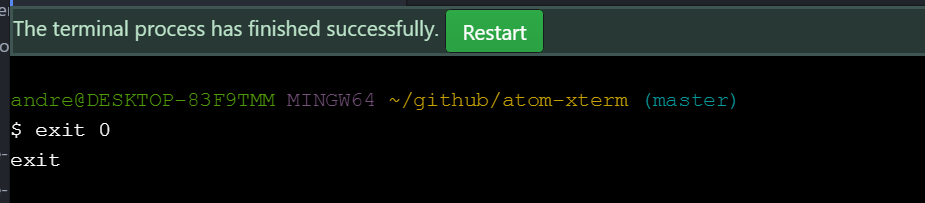
The atom-xterm package provides notifications about terminal process exit successes and failures. Notifications will appear in Atom's own notification manager as well as on the terminal tab triggering the notification.
Success
Failure

There's also activity notifications for terminal tabs not in focus.
Services
For plugin writers, the atom-xterm package supports one service method which
can be used to easily open terminals. This method is provided using Atom's services
API. To use it, add a consumer method to consume the atom-xterm service, or
rather a JavaScript object that provides an
openTerminal() method. The openTerminal() method behaves just like Atom's
open()
method except that the first argument must be a JSON object describing the
terminal profile that should be opened. Docs about this JSON object can be
found here.
As an example on how to use the provided openTerminal() method, your
package.json should have the following.
{
"consumedServices": {
"atom-xterm": {
"versions": {
"^2.0.0": "consumeAtomXtermService"
}
}
}
}
Your package's main module should then define a consumeAtomXtermService
method, for example.
// In ECMAScript 6
import { Disposable } from 'atom'
export default {
atomXtermService: null,
consumeAtomXtermService (atomXtermService) {
this.atomXtermService = atomXtermService
return new Disposable(() => {
this.atomXtermService = null
})
},
// . . .
}
Once the service is consumed, use the openTerminal() method that is provided
by the service, for example.
// Launch `somecommand --foo --bar --baz` in a terminal.
this.atomXtermService.openTerminal({
command: 'somecommand',
args: [
'--foo',
'--bar',
'--baz'
]
})
Development
Want to help develop atom-xterm? Here's how to quickly get setup.
First use the apm command to clone the atom-xterm repo.
apm develop atom-xterm
This should clone the atom-xterm package into the $HOME/github/atom-xterm
directory. Go into this directory and install its dependencies.
cd $HOME/github/atom-xterm
npm install
Rebuild any native binaries that were installed (such as the binaries from the node-pty package) so that they can be used inside Atom.
apm rebuild
Finally, open this directory in Atom's dev mode and hack away.
atom --dev
There's a test suite available for automated testing of the atom-xterm package.
Simply go to View > Developer > Run Package Specs in Atom's main menu or
use the hotkey. You can run the full test suite (which includes running lint
tools) via command-line by running npm run test inside the atom-xterm
directory.
Various lint tools are being used to keep the code "beautified". To run only
the lint tools, simply run npm run lint.
Pull Requests
Whenever you're ready to submit a pull request, be sure to submit it
against a fork of the main atom-xterm repo
master branch that you'll own. Fork the repo using Github and make note of the
new git URL. Set this new git URL as the URL for the origin remote in your
already cloned git repo is follows.
git remote set-url origin ${NEW_GIT_URL}
Ensure your new changes passes the test suite by running npm run test.
Afterwards, push your changes to your repo and then use Github to submit a new
pull request.
xterm.js
The terminals that users interact with in this package is made possible with major help from the xterm.js library. As such, often times it's necessary to make changes to xterm.js in order to fix some bug or implement new features.
If you want to work on xterm.js for the benefit of a bug fix or feature to be supported in atom-xterm, here's how you can quickly get setup.
First make a fork of xterm.js. Next, clone your newly created fork as follows.
git clone ${YOUR_XTERMJS_FORK} ${HOME}/github/xterm.js
Go into your newly cloned repo for xterm.js.
cd ${HOME}/github/xterm.js
Install all needed dependencies.
npm install
Build xterm.js.
npm run build
Ensure the test suite passes.
npm run test
npm run lint
Add a global link for xterm.js to your system.
npm link
Inside your atom-xterm directory, link against the global xterm link.
cd ${HOME}/github/atom-xterm
npm link xterm
Finally, perform a rebuild with the apm program inside the atom-xterm directory.
apm rebuild
You're all set for developing xterm.js. Hack away in your xterm.js directory,
run npm run build, then reload your Atom window to see the changes to your
terminals.
Credits and Legal
See the NOTICE and LICENSE files for copyright and license info about this package respectively.
See the THIRD-PARTY file for info about the dependencies used in the atom-xterm package.
Feedback
Need to submit a bug report? Have a new feature you want to see implemented in atom-xterm? Please feel free to report them through the issues page. For bug reports, please also provide images or demos showing your issues if you can.




